Pugpig Bolt DUTA Model
Table of Contents
Custom Analytics, User data, Tags and Attributes
When a user authenticates, the verify response returns multiple pieces of information specific to that user, in addition to the actual authentication status. These can be broken down into 4 categories
- Analytics Dimensions
- User data
- Tags
- Attributes
The goals of standardising this model are
- Ensure we have a shared understanding of what all of these different types of data are
- Make it clear where this data should get sent, and where it should not get sent
- Standardise as far as possible the implementation of future third-party services to ensure they get sent the right data
Analytics Dimensions
Custom analytics are passed to all third party providers. It will be sent alongside any analytics events. The source of these dimensions is usually the customer’s customer data platform or subscription service, such as Piano or Abacus.
An example of this could be a user’s school or membership level.
Although GA4 advises against the use of high cardinality dimensions (those with more than 500 unique values), analytics dimensions can be used to send values including user ID so that it can be analysed at the event level.
Additionally, we support the concept of feed-based custom analytics dimensions. A common example of this is an article ID
Syntax: http://schema.pugpig.com/custom_analytics/articleID
Passed to
- Everything
User data
User data is specific to the user, and may include PII (personally identifiable information) such as name or email address. This is also how user IDs are passed to other services. User IDs are special-cased for different services, such as Airship where they're used for the Named User functionality and Firebase's User ID.
Firebase's User ID maps to GA4's 'Signed in with user ID' dimension which allows you to compare the behaviour of logged in vs logged out users. The ID is visible via User Explorations alongside a range of summary metrics including session and event count. For information, read Google's documentation.
Syntax for user IDs: http://schema.pugpig.com/user/id
Syntax for other user fields: http://schema.pugpig.com/user/address
Passed to
- Everything. The third parties may or may not then associate this info with events and/or make it available for notification targeting
Tags
Custom tags are multi-value and passed to third party services to enrich a user profile and thus further enable personalisation and segmentation; they “tag” a user as belonging to a certain segment. Examples of this include a user’s membership type. Tags differ from normal analytics in that they can be multi-value; for a specific tag the user can be in multiple segments. Not all providers support tags. Custom tags are not sent with analytics events.
Syntax: http://schema.pugpig.com/custom_tags/animals
Passed to
- Everything that supports the concept
Attributes
Custom attributes never leave the device. The app uses them to provide a more relevant experience to a user. These can be injected into same-origin content views to do things like display membership details.
Syntax: http://schema.pugpig.com/attribute/email
Passed to
- Content view
Not passed to
- Anything off the device
Transfer matrix
The main goal of this initiative is to standardise how we implement SDKs, with all SDKs being of a defined type, and all SDKs of the same type receiving the same data in the same format. You can determine what information should be passed to a given SDK using the below table.
Data type |
Potentially PII |
Analytics |
Push |
CDP |
CMP |
Webviews |
Dimensions |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
User |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Tags |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
Attributes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Notes and Addenda
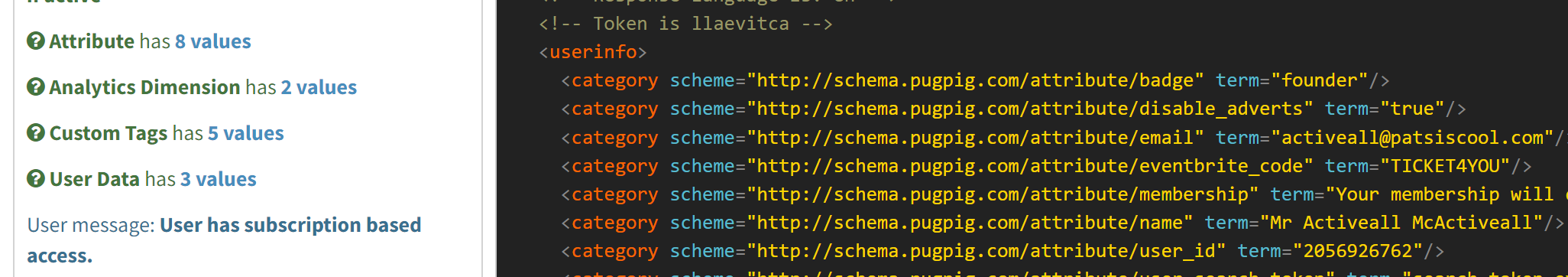
You can see how the return values from your entitlement integration classify each item in the user information block by using the Pugpig Authentication Test Form
Airship Attributes
Airship supports its own concept of attributes but these are totally unrelated to our concept of attributes, which do not leave the device. Airship’s attributes instead map to our user data as described above.
Priority and merging
In the case of a user having multiple forms of access, we only display/send the values for the method with the highest priority, in order these are
- Third-party (your subscription system, i.e Piano)
- Voucher codes
- Store (App Store or Play Store)
Additionally active methods will trump inactive methods. In other words, if you are signed into third-party auth that does not grant you access but have a store subscription that does grant you access, the store information will win.